- Your cart is empty
- Continue shopping
Exploring Ethical, Organic, and Sustainable Business Practices

In this blog post, we embark on a journey to explore the intersection of ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses. We’ll delve into what each of these terms signifies in the context of commerce, and how they collectively shape a more conscientious and environmentally-friendly business world. From shared values and goals to the practical strategies and case studies that exemplify these principles, we will uncover how these concepts overlap and synergize.
The Common Goals and Values
Core Values:
Environmental Responsibility:
This core value centers around the commitment of ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses to reduce their environmental impact. They employ practices that minimize pollution, waste, and the depletion of natural resources. This commitment extends to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water, and protecting biodiversity.
Social Responsibility:
Ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses embrace social responsibility by considering the welfare of their workers and the communities in which they operate. This means ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and opportunities for personal and professional growth for their employees. It also involves community engagement, such as supporting local schools, charities, and environmental initiatives.
Transparency:
Transparency is a fundamental value shared by these businesses. They place a strong emphasis on honest and open communication. This includes disclosing information about their supply chains, sourcing practices, ingredient origins, and production methods. This transparency builds trust with consumers and stakeholders who value knowing where their products come from and how they are made.
Aligning Interests:
Responsible Consumption:
Ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses actively promote responsible consumption. They educate consumers about the impact of their choices on the environment and society. This may include encouraging consumers to buy products with minimal environmental impact or to reduce waste by opting for reusable and recyclable alternatives.
Reduced Environmental Impact:
These businesses collectively work to minimize their environmental impact. This involves adopting eco-friendly production methods, such as using renewable energy, reducing waste and pollution, and sourcing sustainable materials. Their aim is to protect ecosystems, reduce deforestation, and combat climate change.
Supporting Local Communities:
Many ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses prioritise local communities. They support local farmers, artisans, and businesses by sourcing ingredients and materials locally. Additionally, they often engage in community development projects, such as supporting education and healthcare initiatives in their areas of operation.
Building a Strong Foundation:
The Business Advantage:
Embracing these shared values provides a significant advantage for businesses. By aligning with environmental and social responsibility, they can attract a growing segment of consumers who prioritize sustainability and ethics in their purchasing decisions. This not only builds customer loyalty but also enhances brand reputation, potentially resulting in increased sales and profitability.
The Moral Imperative:
Beyond the business advantage, there is a moral imperative associated with these shared values. Ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses recognize that their actions can have a profound impact on the well-being of the planet and society as a whole. They view it as their duty to contribute positively to these spheres, aiming to leave a lasting legacy of responsible and sustainable practices.

The Ethical Business Model
The Ethical Business Model is a framework for operating a business that prioritizes ethical values and principles in its operations, decision-making, and relationships with various stakeholders. Ethical businesses aim to go beyond profit maximization and focus on making a positive impact on society, the environment, and the well-being of all those involved. Here are key components of the Ethical Business Model:
Values and Principles:
Ethical businesses define a set of values and principles that guide their actions. These values often include integrity, honesty, transparency, fairness, and a commitment to social and environmental responsibility.
Social Responsibility:
Ethical businesses take into account the broader social implications of their actions. They consider how their decisions affect employees, customers, suppliers, local communities, and society at large. This includes fair wages, safe working conditions, and giving back to the community.
Environmental Stewardship:
Ethical businesses aim to reduce their environmental impact. They may adopt sustainable practices, reduce waste, and minimize their carbon footprint. This can involve using renewable energy, eco-friendly materials, and reducing pollution.
Transparency:
Transparency is a fundamental aspect of ethical business. It involves open and honest communication with stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and the public. Ethical businesses disclose information about their practices, products, and impact on society and the environment.
Fair Labor Practices:
Ethical businesses treat their employees with respect and fairness. This includes paying fair wages, providing safe working conditions, offering opportunities for growth and development, and ensuring work-life balance.
Fair Trade:
Some ethical businesses engage in fair trade practices, which involve paying fair prices to producers, often in developing countries, for their goods and ensuring that they work in safe and humane conditions.
Consumer Education:
Ethical businesses may also focus on educating consumers about the ethical and sustainable aspects of their products. They provide information to help customers make more informed and responsible choices.
Ethical Supply Chain:
Ethical businesses assess and improve the ethical standards in their supply chains. This involves scrutinizing the practices of suppliers and ensuring they meet ethical criteria.
Ethical Marketing:
Ethical businesses avoid deceptive or manipulative marketing practices and promote their products and services honestly and accurately.
The Ethical Business Model is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it can vary depending on the industry, the size of the business, and the specific values and principles the business chooses to prioritize. Ultimately, the goal of an ethical business is to create a positive and sustainable impact on society, the environment, and all stakeholders, while also maintaining financial viability.
Organic Business Practices
“Organic business practices” refer to a set of environmentally responsible and health-conscious methods that businesses adopt in their operations. These practices are inspired by the principles of organic farming and are designed to reduce the use of synthetic chemicals and promote sustainability.
Key aspects of organic business practices often include:
Natural Ingredients:
Using natural and chemical-free ingredients in the products or services a business offers. For instance, an organic skincare company might use organic herbs and oils instead of synthetic chemicals in their products.
Sustainable Sourcing:
Businesses may focus on sourcing materials and resources in ways that minimize their impact on the environment. This might involve using renewable energy sources, recycling, and reducing waste.
Reducing Environmental Harm:
Embracing practices that aim to minimize pollution, conserve water, and promote biodiversity. For example, an organic winery might use sustainable farming methods to protect the soil and surrounding ecosystems.
Healthy Practices:
Prioritising the health and well-being of consumers. This could involve creating food products without synthetic pesticides or GMOs, ensuring transparency in labeling, and providing options for those with dietary restrictions.
Certification:
Meeting the stringent standards required for organic certification. This involves adhering to specific guidelines to ensure that products or services meet the organic criteria. In Australia, the Australian Organic Certification (AOC) is a prominent certification body that many businesses seek to validate their organic products and practices.
Organic business practices align with the idea that businesses should operate in a way that’s not only profitable but also beneficial to the planet and the people who interact with them. This approach is increasingly popular as consumers become more conscious of their choices and seek products and services that promote health and sustainability.

Organic Business Practices
“Organic business practices” refer to a set of environmentally responsible and health-conscious methods that businesses adopt in their operations. These practices are inspired by the principles of organic farming and are designed to reduce the use of synthetic chemicals and promote sustainability.
Key aspects of organic business practices often include:
Natural Ingredients:
Using natural and chemical-free ingredients in the products or services a business offers. For instance, an organic skincare company might use organic herbs and oils instead of synthetic chemicals in their products.
Sustainable Sourcing:
Businesses may focus on sourcing materials and resources in ways that minimize their impact on the environment. This might involve using renewable energy sources, recycling, and reducing waste.
Reducing Environmental Harm:
Embracing practices that aim to minimize pollution, conserve water, and promote biodiversity. For example, an organic winery might use sustainable farming methods to protect the soil and surrounding ecosystems.
Healthy Practices:
Prioritising the health and well-being of consumers. This could involve creating food products without synthetic pesticides or GMOs, ensuring transparency in labeling, and providing options for those with dietary restrictions.
Certification:
Meeting the stringent standards required for organic certification. This involves adhering to specific guidelines to ensure that products or services meet the organic criteria. In Australia, the Australian Organic Certification (AOC) is a prominent certification body that many businesses seek to validate their organic products and practices.
Organic business practices align with the idea that businesses should operate in a way that’s not only profitable but also beneficial to the planet and the people who interact with them. This approach is increasingly popular as consumers become more conscious of their choices and seek products and services that promote health and sustainability.

Sustainable Business Strategies
Sustainable business strategies are all about making choices that help our planet, our communities, and our businesses thrive for the long run. These strategies focus on finding ways to do business that don’t harm the environment, waste resources, or harm people. Instead, they aim to make a positive impact in three key areas: people, planet, and profit.
People:
Sustainable businesses care about the well-being of their employees, the communities where they operate, and the people who make their products. They provide fair wages, good working conditions, and support local initiatives to create a positive social impact.
Planet:
These strategies prioritize the planet’s health. Sustainable businesses aim to reduce waste, use energy and resources efficiently, and limit pollution. They might invest in renewable energy, recycle more, or choose eco-friendly materials to help protect our environment.
Profit:
Sustainable business strategies are not just about doing good; they also focus on doing well financially. By being eco-friendly and socially responsible, these businesses often attract more customers and investors who want to support ethical and sustainable companies.
The Overlap and Synergy
The overlap and synergy between ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses is a powerful concept that embodies positive change in the business world. Think of it as three puzzle pieces that fit together seamlessly to create a bigger, more beautiful picture.
1. Shared Values Create Synergy:
These businesses share common values that center around doing good for people and the planet. They’re committed to honesty, fairness, and responsibility, whether that means treating workers well, promoting clean farming practices, or reducing their environmental footprint.
2. Where the Three Meet:
There are areas where these values naturally intersect. For example, businesses that prioritize ethical labor practices often lean towards sustainable and organic materials and processes. Like in the above Venn diagram, where the middle part represents a sweet spot of goodness where all three aspects converge.
3. A Win-Win for Everyone:
The synergy between these principles benefits everyone. Businesses adopting all three become more responsible and sustainable, and consumers get to make choices that align with their values. Plus, it’s a win for the environment, as these practices reduce waste and pollution.
4. A Brighter Future:
This overlap is like a glimpse into a brighter, more responsible future. It’s about businesses evolving to be more conscious of their impact on the world, and consumers making informed choices that support these values. Together, it paves the way for a world where businesses, consumers, and the planet can thrive together.
5. Driving Positive Change:
Ultimately, the overlap and synergy between these principles is a force for positive change. It encourages businesses to do better and consumers to support those efforts. It’s a small but important step towards creating a world where businesses are not just about profits but also about making the world a better place for all.
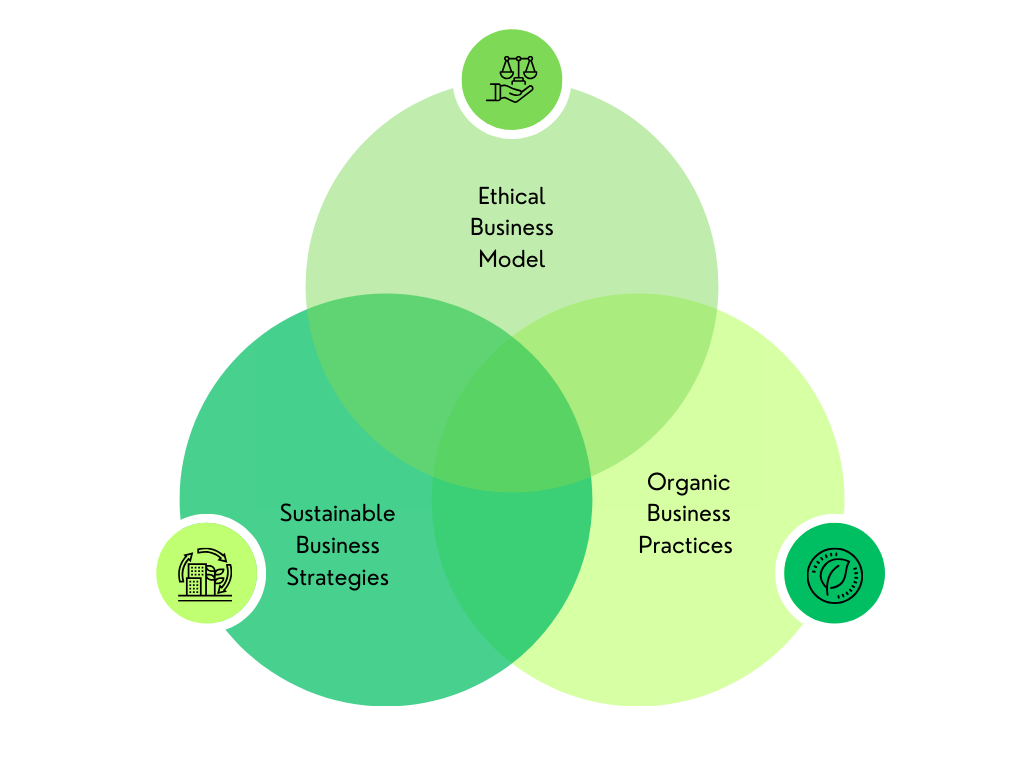
The Overlap and Synergy
The overlap and synergy between ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses is a powerful concept that embodies positive change in the business world. Think of it as three puzzle pieces that fit together seamlessly to create a bigger, more beautiful picture.
1. Shared Values Create Synergy:
These businesses share common values that center around doing good for people and the planet. They’re committed to honesty, fairness, and responsibility, whether that means treating workers well, promoting clean farming practices, or reducing their environmental footprint.
2. Where the Three Meet:
There are areas where these values naturally intersect. For example, businesses that prioritize ethical labor practices often lean towards sustainable and organic materials and processes. Like in the above Venn diagram, where the middle part represents a sweet spot of goodness where all three aspects converge.
3. A Win-Win for Everyone:
The synergy between these principles benefits everyone. Businesses adopting all three become more responsible and sustainable, and consumers get to make choices that align with their values. Plus, it’s a win for the environment, as these practices reduce waste and pollution.
4. A Brighter Future:
This overlap is like a glimpse into a brighter, more responsible future. It’s about businesses evolving to be more conscious of their impact on the world, and consumers making informed choices that support these values. Together, it paves the way for a world where businesses, consumers, and the planet can thrive together.
5. Driving Positive Change:
Ultimately, the overlap and synergy between these principles is a force for positive change. It encourages businesses to do better and consumers to support those efforts. It’s a small but important step towards creating a world where businesses are not just about profits but also about making the world a better place for all.
Consumer Impact and Decision Making
In the world of commerce, your choices as a consumer are like votes. Every time you decide to purchase a product or support a particular business, you’re influencing the direction of that company and even entire industries. Let’s dive into how your decisions matter and the impact they can have:
1. Driving Demand for Ethical, Organic, and Sustainable Businesses:
When you choose to buy from businesses that prioritize ethics, organics, or sustainability, you’re sending a clear message. You’re saying, “I care about how you treat your workers,” or “I want clean and healthy products,” or “I support eco-friendly practices.” Your preferences encourage more businesses to adopt these principles to meet your demands.
2. Holding Businesses Accountable:
Your decisions as a consumer also act as a form of accountability. If a company’s actions or products don’t align with what they claim to stand for, your decision not to support them can make a difference. This encourages businesses to stick to their promises and maintain their ethical, organic, or sustainable commitments.
3. Fostering Positive Change:
By choosing products and businesses that reflect your values, you’re contributing to positive change. Businesses that see their competitors embracing these principles are more likely to follow suit, creating a ripple effect that can ultimately make the marketplace more responsible and environmentally friendly.
4. Contributing to a Healthier World:
Your decision to buy organic products, for instance, promotes healthier farming practices and reduces the use of harmful chemicals. When more people make this choice, it can lead to a shift towards a cleaner, healthier environment.
5. Influencing Industry Trends:
Consumer trends often drive the direction of entire industries. As more people embrace ethical, organic, and sustainable choices, businesses have to adapt to meet these evolving demands. Your choices can shape what’s available on the market.
To maximize your impact, it’s essential to stay informed. Look for certifications, read labels, and do a bit of research on the businesses you support. The more informed your decisions are, the more effectively you can steer the market towards a more responsible and sustainable future.
Challenges and Future Trends
In the ever-evolving landscape of ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses, there are some notable challenges and exciting future trends that deserve our attention. Let’s dive into these in a down-to-earth, human tone:
Challenges
1. Cost Hurdles:
One of the most common obstacles these businesses face is the higher cost associated with ethical, organic, and sustainable practices. From sourcing organic ingredients to paying fair wages, it can be a financial challenge for many smaller enterprises.
2. Market Competition:
As the demand for ethical and sustainable products and services grows, it’s becoming a crowded market. Standing out from the competition and maintaining a customer base can be tough.
Certification Complexities:
Achieving organic or ethical certifications can be a cumbersome process. The paperwork and rigorous standards can sometimes feel overwhelming.
Consumer Misconceptions:
Sometimes, consumers are not fully aware of what these terms mean, which can lead to misconceptions or skepticism. Businesses must educate their customers to build trust.
Future Trends
1. Innovative Packaging:
We’re seeing a shift toward more sustainable and eco-friendly packaging. Expect a surge in innovative, biodegradable, and reusable packaging solutions.
2. Tech-Driven Sustainability:
Technology, like blockchain, is being used to enhance transparency in supply chains. This can help consumers trace the journey of their products, from farm to table.
3. Circular Economy:
More businesses are adopting circular economy models, where waste is minimized, and products are designed to be reused or recycled. It’s all about reducing our environmental footprint.
4. Local Sourcing:
Supporting local communities and reducing transportation emissions is becoming a priority. Look for more businesses to embrace local sourcing for both ingredients and labor.
5. Collaborative Initiatives:
We’re witnessing more partnerships and alliances between businesses, NGOs, and governments to address global sustainability challenges. This collaborative approach is likely to gain momentum.
In a world where conscious consumerism is on the rise, the intersection of ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses holds tremendous promise. These businesses share fundamental values, from environmental stewardship and fair labor practices to transparency and social responsibility. Their collective mission is to create a positive impact on our planet and its inhabitants.
As consumers, we have the power to shape the future by supporting businesses that embody these principles. By making thoughtful choices, we can not only drive demand for ethical, organic, and sustainable products and services but also inspire further innovation and growth in this space.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that these businesses face challenges, such as higher costs and competitive markets. Despite these obstacles, the outlook for the future is optimistic. The dynamic landscape of conscious business is evolving, offering opportunities for continuous improvement and positive change.
Ready to support ethical, organic, and sustainable businesses? Explore them further on EthicalHub, where you can discover and connect with businesses that share these principles. Make a positive impact on the world while making informed choices.



